There are certain things most women are familiar with regarding the menstrual cycle — it can cause bloating, mood swings, cramps, and food cravings. From adolescence until menopause, they’re just a fact of life you learn to live with. But, there are also lesser-known facts about what happens to the body during that time of the month — such as what role does your thyroid play during the entire process?
What is the thyroid?
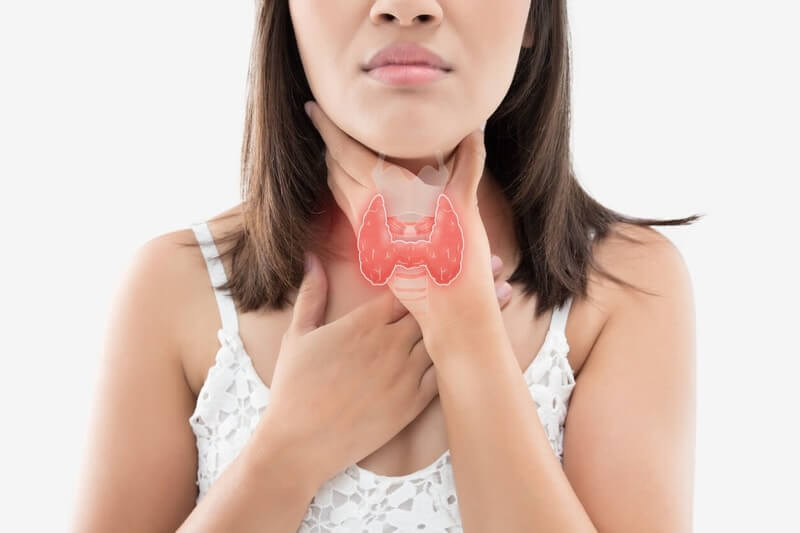
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland at the base of the neck. It’s about two inches long and is part of the body’s endocrine system — a group of glands that produce hormones regulating many of your body’s functions, such as metabolism, sleep patterns, mood, sexual function, and your menstrual cycle. Specifically speaking, the thyroid regulates several functions:
- Metabolism
- Mood
- Heartrate
- Digestion
- Body temperature
When the thyroid doesn’t produce enough hormones, the condition is called hypothyroidism. When a person suffers from hypothyroidism, your heart rate slows down, you gain weight, and experience chronic constipation. On the other end of the spectrum is hyperthyroidism. This occurs when the thyroid releases too many hormones, which results in a rapid heart rate, weight loss, and diarrhea.
How does hypothyroidism affect your menstrual cycle?
A common sign of hypothyroidism is heavier than usual menstrual bleeding. This is because when your thyroid doesn’t make enough hormones, it affects your ovaries’ ability to create progesterone — the hormone that regulates your menstrual cycle. In addition to heavier periods, low progesterone levels make it more difficult to get or to stay pregnant. Low progesterone levels may also cause irregular or absent periods.
Symptoms of Thyroid Disorder
In addition to the symptoms described above, a person with a thyroid disorder may notice changes in all aspects of their health. If you have hyperthyroidism, you’ll experience:
- Feeling constantly tired
- Dry skin
- Feeling cold all the time
- Memory problems
- Depression
- Muscle weakness
Additional symptoms of hyperthyroidism include:
- Restlessness
- Anxiety
- Shaking
- Trouble falling asleep — and staying asleep
- Increased appetite
- Irritability
Treatment Options
For hypothyroidism: Your endocrinologist can prescribe pills containing T4 hormones. Also known as thyroxine, T4 is vital for your overall health, since it aids brain function, bone health, muscle control, and your metabolism. When taking these hormones orally, it’s essential to pay close attention to dosage, since taking too much of it could result in hyperthyroidism.
For hyperthyroidism: Treatment for hyperthyroidism will depend on several factors — such as your age, the severity of the condition, and your medical history. It may include antithyroid drugs. These block the thyroid from over-producing hormones. Another option is by administering radioactive iodine — this shrinks thyroid nodules to return thyroid hormone levels to normal. If conservative forms of treatment do not yield results, your endocrinologist may recommend surgery to remove a portion of the thyroid. Hormone levels can then be restored by taking thyroid hormone supplements.
Contact Us at OB-GYN Women’s Center
At OB-GYN, we aim to establish trusting relationships with our patients. If you have any nagging questions about your reproductive health, don’t be afraid to ask. We are here to help you.
Contact us to schedule an appointment. We’ll answer all of your questions and strive to procure the best treatment for you.